- Meraki Vpn Ios Free
- Meraki Vpn Ios Login
- Meraki Vpn Ios Login
- Cisco Meraki Client Vpn Setup
- Cisco Meraki Vpn Setup
- Meraki Vpn Setup Mac
This article outlines instructions to configure a client VPN connection on commonly-used operating systems. For more information about client VPN, please refer to our Client VPN Overviewdocumentation.
For troubleshooting, please refer to our Troubleshooting Client VPN documentation.
Overview The Meraki Client VPN RADIUS instructions support push, phone call, or passcode authentication for desktop and mobile client connections that use SSL encryption. This configuration does not feature the interactive Duo Prompt for web-based logins. IOS 14 Heads-up After some WTF moments yesterday, I learned that iOS 14 ships with the 'Private Address' per-SSID MAC randomization feature enabled after the update, so anything based on MAC address will break until you either configure the newly generated address for that client, or disable the Private Address feature on each iOS device. VPN Settings This option allows you to pre-configure client-to-gateway VPN connectivity for your iOS, Android (Knox), Mac and Windows devices with support for multiple connection types. Non-Knox Android devices should use solutions like AnyConnect, or apps that support AppConfig app settings like Pulse VPN.
Android
To configure an Android device to connect to the Client VPN, follow these steps:
- Navigate to Settings -> Wireless & Networks -> VPN
- Click the Plus Icon to add an additional VPN profile
Name: This can be anything you want to name this connection, for example, 'Work VPN.'
Type: select L2TP/IPSEC PSK
Server address: Enter the hostname (e.g. .com)orthe active WAN IP (e.g. XXX.XXX.XXX). Hostname is encouraged instead of active WAN IP because it is more reliable in cases of WAN failover. Admin can find them in Dashboard, under Security appliance > Monitor > Appliance status.
IPSec pre-shared key: Enter the pre-shared key that admin created in Security appliance >Configure > Client VPN settings.
Press save
You will be prompted for user credentials when you connect.
Chrome OS
Chrome OS based devices can be configured to connect to the Client VPN feature on MX Security Appliances. This allows remote users to securely connect to the LAN. This article will cover how to configure the VPN connection on a Chrome OS device. For more information on how to setup the Client VPN feature of the MX or how to connect from other operating systems, please visit the MX documentation.
- If you haven't already, sign in to your Chromebook.
- Click the status area at the bottom of your screen, where your account picture is located.
- Select Settings.
- In the 'Internet connection' section, click Add connection.
- Select Add private network.
- In the box that appears, fill in the information below:
- Server hostname:Enter the hostname (e.g. .com)orthe active WAN IP (e.g. XXX.XXX.XXX). Hostname is encouraged instead of active WAN IP because it is more reliable in cases of WAN failover. Admin can find them in Dashboard, under Security appliance > Monitor > Appliance status.
- Service name: This can be anything you want to name this connection, for example, 'Work VPN.'
- Provider type: Select L2TP/IPsec + Pre-shared key.
- Pre-shared key: Enter shared secret that admin created in Security appliance >Configure > Client VPN settings.
- Username credentials for connecting to VPN. If using Meraki authentication, this will be an e-mail address.
- Password credentials for connecting to VPN.
- Click Connect.
For more information regarding the configuration of VPN connections in Chrome OS, visit the Google Support page.
To configure an iOS device to connect to the Client VPN, follow these steps:
- Navigate to Settings -> General-> VPN -> Add VPN Configuration..
- Type: set to L2TP.
- Description:This can be anything you want to name this connection, for example, 'Work VPN.'
- Server: Enter the hostname (e.g. .com)orthe active WAN IP (e.g. XXX.XXX.XXX). Hostname is encouraged instead of active WAN IP because it is more reliable in cases of WAN failover. Admin can find them in Dashboard, under Security appliance > Monitor > Appliance status.
- Account: Enter the username
- Password: Enter if desired. If the password is left blank, it will need to be entered each time the device attempts to connect to the Client VPN.
- Secret: Enter shared secret that admin created in Security appliance >Configure > Client VPN settings.
- Ensure that Send All Traffic is set to On.
- Save the configuration.
macOS
Currently only the following authentication mechanisms are supported:
- User authentication: Active Directory (AD), RADIUS, or Meraki hosted authentication.
- Machine authentication: Preshared keys (a.k.a., shared secret).
When using Meraki hosted authentication, VPN account/user name setting on client devices (e.g., PC or Mac) is the user email address entered in the Dashboard.
The instructions below are tested on Mac OS 10.7.3 (Lion).
Open System Preferences > Network from Mac applications menu. Click the '+' button to create a new service, then select VPN as the interface type, and choose L2TP over IPsec from the pull-down menu.
- Server Address: Enter the hostname (e.g. .com)orthe active WAN IP (e.g. XXX.XXX.XXX). Hostname is encouraged instead of active WAN IP because it is more reliable in cases of WAN failover. Admin can find them in Dashboard, under Security appliance > Monitor > Appliance status.
- Account Name: Enter the account name of the user (based on AD, RADIUS or Meraki Cloud authentication).
- User Authentication > Password: User password (based on AD, RADIUS or Meraki Cloud authentication).
- Machine Authentication > Shared Secret: Enter shared secret that admin created in Security appliance >Configure > Client VPN settings.
The VPN connectivity will not be established if you don't enable the Send all traffic over VPN connection option!
Windows 7
Currently only the following authentication mechanisms are supported:
- User authentication: Active Directory (AD), RADIUS, or Meraki hosted authentication.
- Machine authentication: Preshared keys (a.k.a., shared secret).
When using Meraki hosted authentication, VPN account/user name setting on client devices (e.g., PC or Mac) is the user email address entered in the Dashboard.
Open Start Menu > Control Panel, click on Network and Internet, click on View network status and tasks.
In the Set up a connection or network pop-up window, choose Connect to a workplace (Set up a dial-up or VPN connection to your workplace).
Choose Use my Internet connection (VPN), in the Connect to a workspace dialog window. Citra 1.0 apk.
In the Connect to a Workplace dialog box, enter:
- Internet address: Enter the hostname (e.g. .com)orthe active WAN IP (e.g. XXX.XXX.XXX). Hostname is encouraged instead of active WAN IP because it is more reliable in cases of WAN failover. Admin can find them in Dashboard, under Security appliance > Monitor > Appliance status.
- Destination name:This can be anything you want to name this connection, for example, 'Work VPN.'
Choose 'Don't connect now; just set it up so that I can connect later' option.
Click Next. In the next dialog window, enter the user credentials, and click Create.
Despite the name 'Unencrypted PAP', the client's password is sent encrypted over an IPsec tunnel between the client device and the MX. The password is fully secure and never sent in clear text over either the WAN or the LAN.
Windows 8
Currently only the following authentication mechanisms are supported:
- User authentication: Active Directory (AD), RADIUS, or Meraki hosted authentication.
- Machine authentication: Preshared keys (a.k.a., shared secret).
When using Meraki hosted authentication, VPN account/user name setting on client devices (e.g., PC or Mac) is the user email address entered in the Dashboard.
Open Start Menu > Network and Sharing Center and click Settings.
In the Set Up a Connection or Network pop-up window, choose Connect to a workplace.
(Set up a dial-up or VPN connection to your workplace).
Choose Use my Internet connection (VPN), in the Connect to a Workspace dialog window.
In the Connect to a Workplace dialog box, enter:
- Internet address: Enter the hostname (e.g. .com)orthe active WAN IP (e.g. XXX.XXX.XXX). Hostname is encouraged instead of active WAN IP because it is more reliable in cases of WAN failover. Admin can find them in Dashboard, under Security appliance > Monitor > Appliance status.
- Destination name:This can be anything you want to name this connection, for example, 'Work VPN.'
Go back to Network and Sharing Center and click Change Adapter Settings.
Despite the name 'Unencrypted PAP', the client's password is sent encrypted over an IPsec tunnel between the client device and the MX. The password is fully secure and never sent in clear text over either the WAN or the LAN.
Windows 10
Currently only the following authentication mechanisms are supported:
- User authentication: Active Directory (AD), RADIUS, or Meraki hosted authentication.
- Machine authentication: Preshared keys (a.k.a., shared secret).
When using Meraki hosted authentication, VPN account/user name setting on client devices (e.g., PC or Mac) is the user email address entered in the Dashboard.
Open Start Menu > Search 'VPN' > Click Change virtual private networks (VPN)
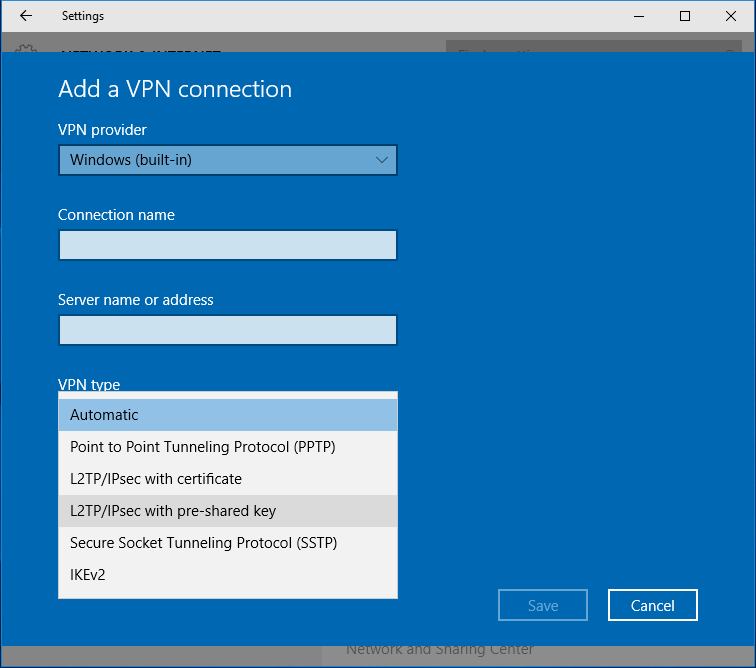
From the VPN settings page, click Add a VPN connection.
In the Add a VPN connection dialog:
- VPN provider: Set to Windows (built-in)
- Connection name: This can be anything you want to name this connection, for example, 'Work VPN.'
- Server name or address: Enter the hostname (e.g. .com)orthe active WAN IP (e.g. XXX.XXX.XXX). Hostname is encouraged instead of active WAN IP because it is more reliable in cases of WAN failover. Admin can find them in Dashboard, under Security appliance > Monitor > Appliance status.
- VPN type: Select L2TP/IPsec with pre-shared key
- User name and Password: optional
Microsoft cleaner for windows 10. Press Save.
After the VPN connection has been created, click Change adapter options under Related settings.
Right-click on the VPN Connection from the list of adapters and click Properties.
Despite the name 'Unencrypted PAP', the client's password is sent encrypted over an IPsec tunnel between the client device and the MX. The password is fully secure and never sent in clear text over either the WAN or the LAN.
In Advanced Properties dialog box, choose 'Use preshared key for authentication' and enter the pre-shared key that admin created in Security appliance >Configure > Client VPN settings.
Back at the Network Connections window, right-click on the VPN connection and click Connect / Disconnect.
Find your VPN profile and click Connect.
Windows XP
Currently only the following authentication mechanisms are supported:
- User authentication: Active Directory (AD), RADIUS, or Meraki hosted authentication.
- Machine authentication: Preshared keys (a.k.a., shared secret).
When using Meraki hosted authentication, use the email address for VPN account / user name.
Open Start Menu > Control Panel, click on Network Connections.
In the Network Tasks section, click on Create a new connection.
Choose Connect to the network at my workplace, in the New Connection Wizard window.
Choose Virtual Private Network connection in the next section.
Then, give a name for this connection. This can be anything you want to name this connection, for example, 'Work VPN.'
Enter the hostname (e.g. .com)orthe active WAN IP (e.g. XXX.XXX.XXX). Hostname is encouraged instead of active WAN IP because it is more reliable in cases of WAN failover. Admin can find them in Dashboard, under Security appliance > Monitor > Appliance status.
In the Connect <Connection Name> box, click on Properties
In the General tab, verify the hostname (e.g. .com)orthe active WAN IP (e.g. XXX.XXX.XXX). Hostname is encouraged instead of active WAN IP because it is more reliable in cases of WAN failover. Admin can find them in Dashboard, under Security appliance > Monitor > Appliance status.
Despite the name 'Unencrypted PAP', the client's password is sent encrypted over an IPsec tunnel between the client device and the MX. The password is fully secure and never sent in clear text over either the WAN or the LAN.
Since Client VPN uses the L2TP over IPsec standard, any Linux client that properly supports this standard should suffice. Please note that newer versions of Ubuntu do not ship with a VPN client that supports L2TP/IP, and will therefore require a 3rd party VPN client that supports the protocol.
Note: The xl2tp package does not send user credentials properly to the MX when using Meraki Cloud Controller authentication, and this causes the authentication request to fail. Active Directory or RADIUS authentication can be used instead for successful authentication.
Configuring Ubuntu 20.04
Ubuntu does not support L2TP VPN by default. You will need to install a couple of software packages to enable this functionality. The instructions below were written for Ubuntu 20.04 LTS with the Gnome desktop environment. Ubuntu versions 16.04 and 18.04 can be configured in a similar manner. However, due to the large number of Linux versions available, it is not feasible to document every supported Ubuntu version.
In order to begin the VPN setup, open up a terminal window. Do this by searching for Terminal in your application list. Click on the Terminal icon to open a new terminal session.
Once the terminal window appears, you will need to enter a few commands.
Note: You will need to be a part of the “sudoers” group to install these packages. If you receive an error message like “<username> is not in the sudoers file.” you will need to either adjust your permissions, contact your administrator to add your account as an administrator or have them install the software for you.
Once the packages have been installed, you may open up the Network Settings by searching for Settings in the application list, or by clicking on the Network icon at the top right of the screen and selecting Wired (or Wireless) Settings.
Once the Network Settings window pops up, you will see there is a VPN section listed. Click on the + icon to set up a new VPN connection.
Select the Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) VPN type on the modal pop up window. If L2TP is not listed as an option, please see the first step about installing the required packages.
After selecting the L2TP option, a new modal will pop up titled Add VPN. Fill out your VPN Name, Gateway, User name, and Password information here.
Note: To save your password on this screen, you must select the appropriate option from the question mark on the password field.
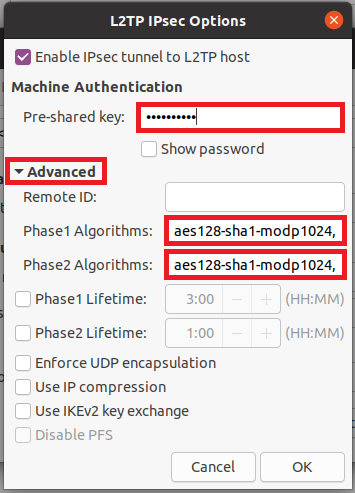
Next, click on the IPsec Settings button to open the L2TP IPsec Options modal.
Once the modal pops up, expand the Advanced options, and enter the following:
Select OK to continue. You will be returned back to the Add VPN modal. Select the PPP Settings button.
On the L2TP PPP Options modal, select only the PAP authentication method. Be sure the other authentication methods are de-selected. All other options can remain as the default. Select OK to continue.
Select Add at the top right corner of the Add VPN modal to complete the VPN setup.
Now you may connect your VPN by toggling the button on the Network Settings page:
Or by selecting the Connect option from the top right corner menu.
Upon successful connection, a VPN icon will appear next to the network icon in the status bar.
Meraki Vpn Ios Free
Note: The version of network-manager-l2tp that is installed along with xl2tpd is known to cause issues when connecting to Meraki Appliances. To alleviate this, you must disable the xl2tpd service when using the network-manager GUI to connect to a Meraki VPN.
Meraki Vpn Ios Login
To stop the xl2tpd service once use this Terminal command:

sudo service xl2tpd stop
To stop the xl2tpd service for all subsequent reboots use this Terminal command:
Meraki Vpn Ios Login
sudo update-rc.d xl2tpd disable
Cisco Meraki’s unique auto provisioning site-to-site VPN connects branches securely, without tedious manual VPN configuration. Leveraging the power of the cloud, MX Security Appliances configure, monitor, and maintain your VPN so you don't have to.
Cisco Meraki’s unique auto provisioning site-to-site VPN connects branches securely with complete simplicity. Using IPsec over any wide area network, the MX links your branches to headquarters as well as to one another as if connected with a virtual Ethernet cable. Customers accessing or moving services to the Amazon Web Services cloud can use Auto VPN to connect directly to a virtual MX inside their Virtual Public Cloud.
MX Security Appliances automatically configure VPN parameters needed to establish and maintain VPN sessions. A unique cloud-enabled hole-punching and discovery mechanism enables automatic interconnection of VPN peers and routes across the WAN, and keeps them updated in dynamic IP environments. Security associations and phases, authentication, key exchanges, and security policies are all handled automatically by MX VPN peers. Site-to-site connectivity is established through a single click in the Cisco Meraki dashboard. Intuitive tools built in to the Cisco Meraki dashboard give administrators a real-time view of VPN site connectivity and health. Round trip time latency between peers and availability status information automatically keep track of all the VPN peers in the network.
Cisco Meraki Client Vpn Setup
Flexible tunneling, topology, and security policies
Cisco Meraki Vpn Setup
Configurations for split-tunneling and full-tunneling back to a concentrator at headquarters are fully supported and configured in a single click. Hub-and-spoke and full mesh VPN topologies give deployment flexibility, and a built-in site-to-site firewall enables custom traffic and security policies that govern the entire VPN network.
Meraki Vpn Setup Mac
Cloud Managed Security Appliances
See features, specifications, and pricing for Cloud Managed Security Appliances.
